K8 Istio little Deep Dive
I’ve been playing a little bit with Istio mostly egress , but today i wanted to write about ingresses .
Basically Istio ingresses are a number of proxies (envoy) that kind of talk to each other to deal with access , throttling and app routing in general.
What is really interesting about the istio approach is the sidecar injection, imagine that you’re running a container execs nginx (port80 )S
What istio does is “inject” a sidecar container , that runs on the same pod , that means , sharing the kernel network namespace with privileged mode and NET_ADMIN capabilities.
That way , they guarantee full tracing of services for example or mutual tls for example.
In very simple terms it looks like this:
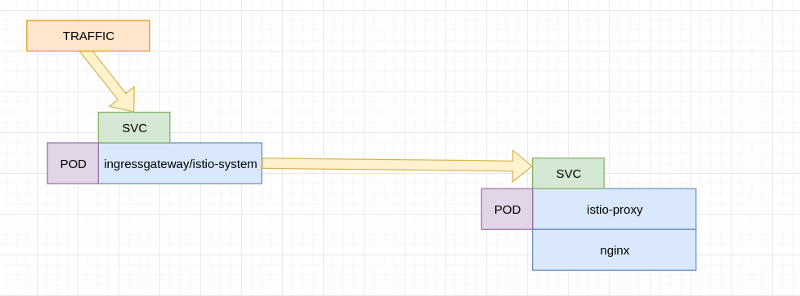 Istio workflow
Istio workflow
This is much different than having a traditional nginx ingress , the nginx ingress speaks to a service that iptables to a pod , for example:
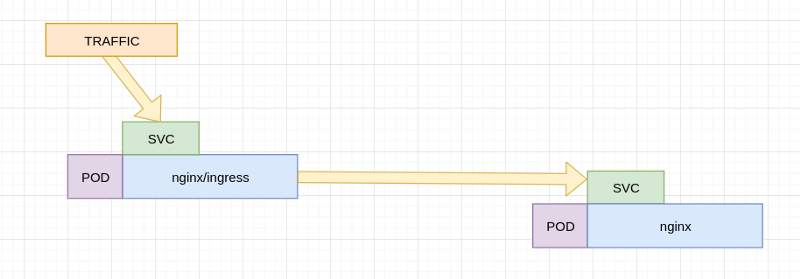 nginx ingress workflow
nginx ingress workflow
So what’s the main difference? well that side container , it’s called istio-proxy and it “INTERCEPTS” traffic , i was particularly interested in the way that this intercepts traffic .
The hint is when you see:
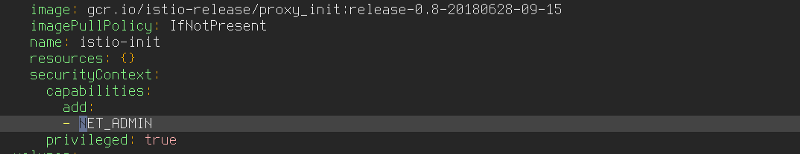
That means that within the struct net that the kernel namespace represents ( or pod) , this container needed to be privileged and have NET_ADMIN , this is especially important if your mangling ti SOCK options like IP_TRANSPARENT or managing IPTables rules , not for the kube host , but for the struct net bound the pod.
So if you created your pod with nginx listening on 8000 and injected it with istioctl , the iptables on the side car will look like(note you have to enter it with privileged mode enabled docker exec — privileged -it 75375f8d4c98 bash)
root@nginx-847679bd76-mj4sw:~# iptables -t nat -S
-P PREROUTING ACCEPT
-P INPUT ACCEPT
-P OUTPUT ACCEPT
-P POSTROUTING ACCEPT
-N ISTIO_INBOUND
-N ISTIO_OUTPUT
-N ISTIO_REDIRECT
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -j ISTIO_INBOUND
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -j ISTIO_OUTPUT
-A ISTIO_INBOUND -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ISTIO_REDIRECT
-A ISTIO_OUTPUT ! -d 127.0.0.1/32 -o lo -j ISTIO_REDIRECT
-A ISTIO_OUTPUT -m owner --uid-owner 1337 -j RETURN
-A ISTIO_OUTPUT -m owner --gid-owner 1337 -j RETURN
-A ISTIO_OUTPUT -d 127.0.0.1/32 -j RETURN
-A ISTIO_OUTPUT -j ISTIO_REDIRECT
-A ISTIO_REDIRECT -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports 15001
Now it’s clear that this is redirecting all incoming traffic into 80 to 150001 , which is bonud by istio-proxy , envoy does it works and it will send traffic to nginx(80).
netstat shows:
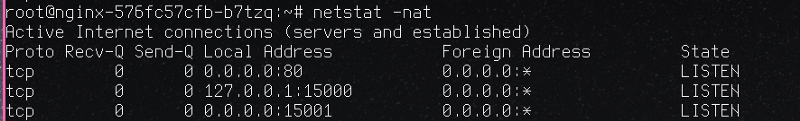
15001 is there , let’s see tcpdump:
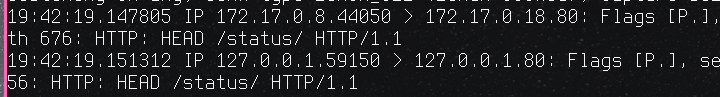
So initially there’s traffic coming to port 80 , but it gets redirected to localhost:15001 , that’s envoy , next step is actually send traffic to nginx itelf , that’s why we see a double “HEAD” request , 1 to envoy (forced by iptales ) and 1 to nginx.
I’l write a little more about how to set all the ingress elements later on.
